Abstract
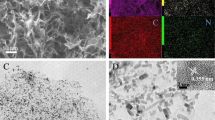
In this study, dual functional conductive hydrogels containing polypyrrole (PPy) nanotubes (NTs) functionalized with beta-cyclodextrin (bCD) and titania (TiO2) were produced and applied for both detection and removal of toxic substances. PPy, a representative conducting polymer was prepared in a form of nanotube (NT) and used for providing electrical conductivity. TiO2 nanoparticles were incorporated into the inside of the PPy NTs during the formation of PPy NTs, acting as a photocatalyst. Subsequently, beta-cyclodextrin (bCD) molecules were introduced as sensing media on the surface of PPy NTs via a simple surface treatment. The resulting TiO2@PPy-bCD hybrid NTs were embedded into agarose matrix to obtain a conductive hydrogel, simultaneously improving compatibility with substrates. The electrical properties of the hydrogel were investigated, showing electrical conductivity of approximately 10−3 S/cm and ohmic I-V relation on Au electrode. The sensing capability for a model analyte compound (methyl paraben, MPRB) down to 10 nM and photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue (MB) were demonstrated effectively. This study can provide important information for upcoming research activities for environmentally benign and toxic free versatile chemical sensors in diverse relevant fields.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Xiang, C., Jiang, D., Zou, Y., Chu, H., Qiu, S., Zhang, H., Xu, F., Sun, L., Zheng, L.: Ammonia sensor based on polypyrrole–graphene nanocomposite decorated with titania nanoparticles. Ceramics Int. 41, 6432–6438 (2015)
Ramesan, M.T., Santhi, V., Bahuleyan, B.K., Al-Maghrabi, M.A.: Structural characterization, material properties and sensor application study of in situ polymerized polypyrrole/silver doped titanium dioxide nanocomposites. Mater. Chem. Phys. 211, 343–354 (2018)
Xiaohui, T., Raskin, J.-P., Lahem, D., Krumpmann, A., Decroly, A., Debliquy, M.: A formaldehyde sensor based on molecularly-imprinted polymer on a TiO2 nanotube array. Sensors 17, 675 (2017)
Mehdinia, A., Shoormeij, Z., Jabbari, A.: Trace determination of lead(II) ions by using a magnetic nanocomposite of the type FeO/TiO/PPy as a sorbent, and FAAS for quantitation. Microchim. Acta 184, 1529–1537 (2017)
Yu, M., Wu, L., Miao, J., Wei, W., Liu, A., Liu, S.: Titanium dioxide and polypyrrole molecularly imprinted polymer nanocomposites based electrochemical sensor for highly selective detection of p-nonylphenol. Anal. Chim. Acta 1080, 84–94 (2019)
Bulakhe, R.N., Patil, S.V., Deshmukh, P.R., Shinde, N.M., Lokhande, C.D.: Fabrication and performance of polypyrrole (Ppy)/TiO2 heterojunction for room temperature operated LPG sensor. Sens. Actuat. B Chem. 181, 417–423 (2013)
Li, X., He, G., Han, Y., Xue, Q., Wu, X., Yang, S.: Magnetic titania-silica composite–Polypyrrole core–shell spheres and their high sensitivity toward hydrogen peroxide as electrochemical sensor. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 387, 39–46 (2012)
Hamtak, M., Fotouhi, L., Hosseini, M., Reza, G.: Sensitive nonenzymatic electrochemiluminescence determination of hydrogen peroxide in dental products using a polypyrrole/polyluminol/titanium dioxide nanocomposite. Anal. Lett. 52, 633–648 (2019)
Zhang, T., Ma, N., Ali, A., Wei, Q., Wu, D., Ren, X.: Electrochemical ultrasensitive detection of cardiac troponin I using covalent organic frameworks for signal amplification. Biosens. Bioelect. 119, 176–181 (2018)
Xie, Y., Zhao, Y.: Electochemical biosensing based on polypyrrole/titania nanotube hybrid. Mater. Sci. Eng. 33, 5028–5035 (2013)
AL-Mokaram, A., Yahya, R., Abdi, M.M., Ekramul Mahmud, H.N.M.: The development of non-enzymatic glucose biosensors based on electrochemically prepared polypyrrole-chitosan-titanium dioxide nanocomposite films. Nanomater. 7, 129 (2017)
Hwang, Y., Park, J.Y., Kwon, O.S., Joo, S., Lee, C.-S., Bae, J.: Incorporation of hydrogel as a sensing medium for recycle of sensing material in chemical sensors. Appl. Surf. Sci. 429, 258–263 (2018)
Hwang, Y., Park, J.Y., Lee, C.-S., Kwon, O.S., Park, S.-H., Bae, J.: Surface engineered poly(dimethylsiloxane)/carbon nanotube nanocomposite pad as a flexible platform for chemical sensors. Compos. A 107, 55–60 (2018)
Park, S.J., Lee, J., Seo, S.E., Kim, K.H., Park, C.S., Lee, S.H., Ban, H.S., Lee, B.D., Song, H.S., Kim, J., Lee, C.-S., Bae, J., Kwon, O.S.: High-performance conducting polymer nanotube-based liquid-ion gated field-effect transistor aptasensor for dopamine exocytosis. Sci. Rep. 10, 3772 (2020)
Bae, J., Hwang, Y., Ha, J.-H., Kwon, O.S., Jang, A., Kim, H.J., An, J., Lee, C.-S., Park, S.-H.: Versatile chemical sensors using oligosaccharides on cleanable PDMS/graphene hybrids for monitoring environmentally hazardous substances. Appl. Surf. Sci. 507, 145139 (2020)
Bae, J., Shin, K., Kwon, O.S., Hwang, Y., An, J., Jang, A., Kim, H.J., Lee, C.-S.: A succinct review of refined chemical sensor systems based on conducting polymer–cyclodextrin hybrids. J. Ind. Eng. Chem. 79, 19–28 (2019)
Li, X., Sun, J., He, G., Jiang, G., Tan, Y., Xue, B.: Macroporous polypyrrole-TiO2 composites with improved photoactivity and electrochemical sensitivity. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 411, 34–40 (2013)
Luo, Q., Li, X., Wang, D., Wang, Y., An, J.: Photocatalytic activity of polypyrrole/TiO nanocomposites under visible and UV light. J. Mater. Sci. 46, 1646–1654 (2011)
Sun, L., Shi, Y., Li, B., Li, X., Wang, Y.: Preparation and characterization of polypyrrole/TiO2 nanocomposites by reverse microemulsion polymerization and its photocatalytic activity for the degradation of methyl orange under natural light. Polym. Compos. 34, 1076–1080 (2013)
He, M.Q., Bao, L.L., Sun, K.Y., Zhao, D.X., Li, W.B., Xia, J.X., Li, H.M.: Synthesis of molecularly imprinted polypyrrole/titanium dioxide nanocomposites and its selective photocatalytic degradation of rhodamine B under visible light irradiation. Express Polym. Lett. 8, 850–861 (2014)
Cao, S., Zhang, H., Song, Y., Zhang, J., Yang, H., Jiang, L., Dan, Y.: Investigation of polypyrrole/polyvinyl alcohol–titanium dioxide composite films for photo-catalytic applications. Appl. Surf. Sci. 342, 55–63 (2015)
Macedo, E.R., Oliveira, P.S., de Oliveira, H.P.: Synthesis and characterization of branched polypyrrole/titanium dioxide photocatalysts. J. Photochem. Photobio. A Chem. 307, 108–114 (2015)
Park, S.J., Kwon, O.S., Lee, J.E., Jang, J., Yoon, H.: Conducting polymer-based nanohybrid transducers: a potential route to high sensitivity and selectivity sensors. Sensors 14, 3604–3630 (2014)
Kratofil, K.L., Stjepanović, J., Perlog, M., Krehula, S., Gilja, V., Travas-Sejdic, J., Hrnjak-Murgić, Z.: Conducting polymer polypyrrole and titanium dioxide nanocomposites for photocatalysis of RR45 dye under visible light. Polym. Bull. 76, 1697–1715 (2019)
Ullah, H.H., Tahir, A.A., Mallick, T.K.: Polypyrrole/TiO2 composites for the application of photocatalysis. Sens. Actuat. B Chem. 241, 1161–1169 (2017)
Gu, Y.-J., Wen, W., Xu, Y., Wu, J.-M.: Pyrrole-regulated precipitation of titania nanorods on polymer fabrics for photocatalytic degradation of trace toluene in air. Appl. Surf. Sci. 434, 1055–1063 (2018)
Tan, Y., Chen, Y., Mahimwalla, Z., Johnson, M.B., Sharma, T., Brüning, R., Ghandi, K.: Novel synthesis of rutile titanium dioxide–polypyrrole nano composites and their application in hydrogen generation. Syn. Met. 189, 77–85 (2014)
Ngaboyamahina, E., Cachet, H., Pailleret, A., Sutter, E.M.M.: Photo-assisted electrodeposition of an electrochemically active polypyrrole layer on anatase type titanium dioxide nanotube arrays. Electrochim. Acta 129, 211–221 (2014)
Arenas, M.C., Rodriguez-Nunez, L.F., Rangel, D., Martinez-Alvarez, O., Martinez-Alonso, C., Castano, V.M.: Simple one-step ultrasonic synthesis of anatase titania/polypyrrole nanocomposites. Ultrasonics Sonochem. 20, 777–784 (2013)
Ravikiran, Y.T., Vijaya Kumari, S.C.: Analysis of x-ray diffraction pattern and complex plane impedance plot of polypyrrole/titanium dioxide nanocomposite: a simulation study. AIP Conf. Proc. 1536, 49–50 (2013)
Oliveira, A., Oliveira, H.: Optimization of photocatalytic activity of PPy/TiO nanocomposites. Polym. Bull. 70, 579–591 (2013)
Singh, S.K., Shukla, R.K.: Optical and photoconductivity properties of pure Polypyrrole and titanium dioxide-doped Polypyrrole nanocomposites. Mater. Sci. Semicon. Process. 31, 245–250 (2015)
de Oliveira, A.H.P., de Oliveira, H.P.: Carbon nanotube/polypyrrole nanofibers core-shell composites decorated with titanium dioxide nanoparticles for supercapacitor electrodes. J. Power Sources 268, 45–49 (2014)
Du, H., Xie, Y., Xia, C., Wang, W., Tian, F., Zhou, Y.: Preparation of a flexible polypyrrole nanoarray and its capacitive performance. Mater. Lett. 132, 417–420 (2014)
Jiang, L., Lu, X., Xie, C., Wang, G., Zhang, H., Youhong, T.: Flexible, free-standing TiO2−graphene−polypyrrole composite films as electrodes for supercapacitors. J. Phys. Chem. C 119, 3903–3910 (2015)
Gupta, A., Varshney, S., Goyal, A., Sambyal, P., Kumar Gupta, B., Dhawan, S.K.: Enhanced electromagnetic shielding behaviour of multilayer graphene anchored luminescent TiO2 in PPY matrix. Mater. Lett. 158, 167–169 (2015)
Yoon, C.-M., Cho, K.H., Jang, Y., Kim, J., Lee, K., Yu, H., Lee, S., Jang, J.: Synthesis and electroresponse activity of porous polypyrrole/silica−titania core/shell nanoparticles. Langmuir 34, 15773–15782 (2018)
Bae, J., Hur, J.: Synthesis and characterization of thermo-reversible conductive hydrogel toward smart electrodes. Sci. Adv. Mater. 8, 176–179 (2016)
Bae, J., Hwang, Y., Park, S.-H., Park, S.J., Lee, J., Kim, H.J., Jang, A., Park, S., Kwon, O.S.: An elaborate sensor system based on conducting polymer-oligosaccharides in hydrogel and the formation of inclusion complexes. J. Ind. Eng. Chem (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jiec.2020.07.023. (In press)
Xuan Dat Mai, N., Bae, J., Kim, I.T., Park, S.-H., Lee, G.-W., Kim, J.H., Lee, D., Son, H.B., Lee, Y.-C., Hur, J.: A recyclable, recoverable, and reformable hybrogel-based smart photocatalyst. Environ. Sci. Nano 4, 955–966 (2017)
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by National Research Foundation of Korea, Grant Numbers NRF-2019R1F1A1058571. This work was also supported by Korea Institute of Planning and Evaluation for Technology in Food, Agriculture and Forestry (IPET) through Advanced Production Technology Development Program, funded by Ministry of Agriculture, Food and Rural Affairs (MAFRA) (318104-3) and KRIBB Initiative Research Program.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
JB: corresponding, conceptualization, data curation, funding acquisition, investigation, methodology, project admin, supervision, writing draft. SJP: conceptualization, investigation, methodology, writing review editing. D-SS: investigation, writing review editing. JL: investigation, writing draft. SP: investigation. HJK: investigation. OSK: corresponding, conceptualization, funding acquisition, investigation, methodology, project admin, resources, supervision, writing review editing.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declared that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bae, J., Park, S.J., Shin, DS. et al. A Dual Functional Conductive Hydrogel Containing Titania@Polypyrrole-Cyclodextrin Hybrid Nanotubes for Capture and Degradation of Toxic Chemical. BioChip J 15, 162–170 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13206-021-00015-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13206-021-00015-2